

对一些心肺疾病或手术,使用肝素等药物预防血栓已经是司空见惯的诊疗常规,但是使用药物抗凝的患者在术中止血就成了大问题,抗凝或抗血栓显然会导致血凝块不易形成,伤口不易愈合,出血风险增大。不过研究者已经找到了解决该问题的新方法。
目前的医疗方案中,医生可以采取以下几种方法来减少使用肝素和其他血液稀释剂的患者的术中出血,包括压迫、缝合线、止血纱等。但是这些措施都存在潜在严重风险,一些会给患者带来毒副作用,导致过敏反应或组织坏死。
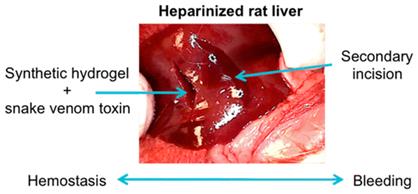
为了更好的解决该问题,D. Hartgerink和他的同事从蛇毒液中提出一种酶,可以促进血液凝固,就算是“肝素”存在条件下,效果依旧很棒。这个酶就是大家都熟悉的“巴曲酶”,在临床上应用已经更广泛了。因为该酶会被快速溶解游离到各处,所以用它术中止血还是存在一定问题。
不过,聪明的研究者想出了阻止巴曲酶分散的好方法,使用纳米纤维材料让“粘住”巴曲酶。该种方式的治疗已经在使用肝素的老鼠上初显成效。
研究者称,该种方法在以后会让使用肝素的患者的手术更加安全。(来源:生物360)
Nanofibrous Snake Venom Hemostat
Abstract Controlling perioperative bleeding is of critical importance to minimize hemorrhaging and fatality. Patients on anticoagulant therapy such as heparin have diminished clotting potential and are at risk for hemorrhaging. Here we describe a self-assembling nanofibrous peptide hydrogel (termed SLac) that on its own can act as a physical barrier to blood loss. SLac was loaded with snake-venom derived Batroxobin (50 μg/mL) yielding a drug-loaded hydrogel (SB50). SB50 was potentiated to enhance clotting even in the presence of heparin. In vitro evaluation of fibrin and whole blood clotting helped identify appropriate concentrations for hemostasis in vivo. Batroxobin-loaded hydrogels rapidly (within 20s) stop bleeding in both normal and heparin-treated rats in a lateral liver incision model. Compared to standard of care, Gelfoam, and investigational hemostats such as Puramatrix, only SB50 showed rapid liver incision hemostasis post surgical application. This snake venom-loaded peptide hydrogel can be applied via syringe and conforms to the wound site resulting in hemostasis. This demonstrates a facile method for surgical hemostasis even in the presence of anticoagulant therapies.
原文链接:http://pubs.acs.org/doi/ipdf/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.5b00356



